Marie stared at her electricity bill in disbelief. €180 for a single month in her small apartment. Her neighbor knocked on the door that evening, excited to share something incredible he’d discovered online. “There’s this guy in France who hasn’t paid an electricity bill in eight years,” he said, pulling up a video on his phone. “He powers his entire house with old laptop batteries.”
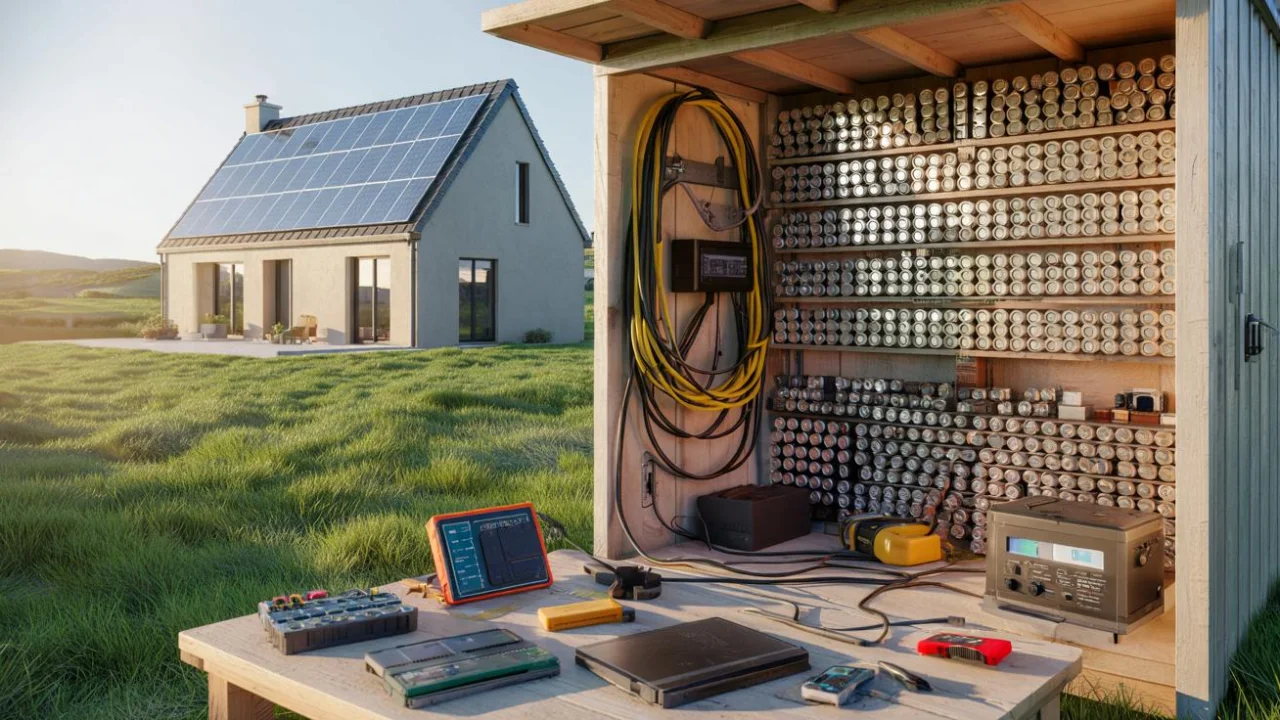
At first, Marie thought it sounded like complete nonsense. How could discarded laptop batteries possibly run a home? But as she watched the footage of a ordinary-looking shed filled with carefully arranged battery modules, something clicked. This wasn’t just about saving money—it was about taking control.
What started as one man’s experiment with electronic waste has quietly become a fascinating example of DIY energy independence that’s inspiring households around the world.
The Shed That Changed Everything
Back in 2016, a French inventor faced the same frustration millions of homeowners know too well: skyrocketing electricity costs and limited options for energy storage. He already had solar panels installed, but when the sun disappeared, so did his power independence.
That’s when he looked at something most people throw away without a second thought: old laptop batteries. These discarded power packs, considered worthless by their previous owners, still contained individual lithium-ion cells with plenty of life left in them.
“Instead of seeing e-waste, he saw opportunity,” explains Dr. Sarah Chen, an energy storage researcher at MIT. “Many laptop batteries lose capacity over time, but the individual cells inside often retain 70-80% of their original power.”
The project started small in a corner of his garage. But as word spread and more people donated their old laptop batteries, the collection grew rapidly. Within just a few years, over 1,000 laptop batteries had passed through his hands. About 650 of them proved suitable for his ambitious laptop battery power system.
The rest? They went to proper recycling facilities, ensuring nothing truly went to waste.
How a Laptop Battery Power System Actually Works
Building a functional laptop battery power system isn’t as simple as connecting a bunch of old batteries together. Each laptop battery contains multiple lithium-ion cells, typically the cylindrical 18650 format that’s become the gold standard for energy storage.
The process involves carefully extracting usable cells, testing their capacity, and organizing them into balanced modules. Here’s what the complete system looks like:
| Component | Function | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| 18650 Battery Cells | Energy storage | ~3,900 cells from 650 batteries |
| Battery Management System | Safety monitoring | Multiple units |
| Inverters | DC to AC conversion | 3 units |
| Charge Controllers | Solar panel integration | 2 units |
| Safety Systems | Fire prevention | Multiple sensors |
The entire laptop battery power system now sits in a dedicated shed, about 50 meters from his house. This distance isn’t accidental—it’s a crucial safety measure when dealing with large amounts of stored energy.
“The key to any successful battery project is respect for the technology,” notes energy consultant Mark Rodriguez. “Lithium-ion cells are incredibly powerful, but they demand proper handling and monitoring.”
- Each cell is individually monitored for temperature and voltage
- Automatic shutdown systems activate if any parameter goes out of range
- Fire suppression equipment is strategically placed throughout the shed
- Ventilation systems prevent gas buildup
- Regular capacity testing ensures system reliability
The Numbers That Will Shock You
After eight years of continuous operation, the results speak for themselves. This laptop battery power system has completely eliminated his electricity bills while providing reliable power for everything from LED lights to washing machines.
The total storage capacity reached approximately 40 kilowatt-hours—enough to power an average European home for several days without any solar input. During sunny periods, the system charges from rooftop solar panels and feeds excess energy back into the house.
“What’s remarkable isn’t just that it works, but how well it’s held up over time,” explains renewable energy engineer Lisa Park. “Commercial battery systems often see significant degradation after five years, but this DIY setup is still running strong.”
The financial impact is equally impressive. While a commercial home battery system of similar capacity would cost €25,000 to €40,000, this project required only the cost of supporting equipment like inverters and charge controllers. The batteries themselves were essentially free waste materials.
Why This Matters for Everyone
This isn’t just an interesting story about one person’s ingenuity. It highlights a massive opportunity hiding in plain sight. Millions of laptop batteries end up in landfills every year, taking their lithium-ion cells with them.
Meanwhile, the demand for home energy storage continues to explode. Countries across Europe are implementing policies to encourage battery installations, but costs remain prohibitive for many households.
The laptop battery power system concept offers a bridge between these two problems. While not everyone has the technical skills to replicate this exact project, it demonstrates the untapped potential in electronic waste streams.
“We’re essentially throwing away the raw materials for our energy transition,” argues environmental engineer Dr. James Thompson. “Projects like this show us what’s possible when we start thinking differently about waste.”
Several companies have already started exploring commercial applications of this approach, developing systems that use recycled laptop batteries for grid-scale storage projects.
The Reality Check
Before anyone rushes to their nearest electronics recycling bin, it’s important to understand the challenges involved. Building a laptop battery power system requires significant electrical knowledge, proper safety equipment, and considerable time investment.
Working with lithium-ion batteries can be dangerous without proper precautions. Fire, explosion, and toxic gas risks are all real concerns that must be managed through careful design and monitoring.
Additionally, not all laptop batteries are created equal. Many modern laptops use different battery chemistries or configurations that may not be suitable for this type of project.
Still, the core concept remains sound. As battery recycling technology improves and regulations evolve, we’re likely to see more innovative approaches to giving these power sources a second life.
FAQs
Is it legal to build a laptop battery power system at home?
In most countries, building personal energy storage systems is legal, but local electrical codes and permits may be required for grid-connected systems.
How dangerous is working with old laptop batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries can be hazardous if damaged or improperly handled, potentially causing fires or releasing toxic gases. Proper safety equipment and knowledge are essential.
Can any laptop battery be used for this type of project?
Not all laptop batteries are suitable. The cells must retain sufficient capacity and be compatible with the chosen system design.
How much money could someone save with a laptop battery power system?
Savings depend on local electricity costs and system size, but complete energy independence could eliminate monthly electricity bills entirely.
Do these recycled batteries last as long as new ones?
While used batteries have reduced capacity compared to new ones, quality cells can still provide years of reliable service in home storage applications.
Where can someone find enough old laptop batteries for this type of project?
Electronics recycling centers, computer repair shops, schools, and businesses often have large quantities of discarded laptop batteries available.